Syngeneic mouse models offer an ideal platform for conducting early proofs of concept to test immune-oncology (IO) therapeutics within the context of an intact and fully functional immune system. In these models, tumor tissue is sourced from a donor mouse that shares the exact genetic background with the recipient immune-competent mouse. This genetic compatibility ensures that the tumor microenvironment and transplanted cells match the host, making syngeneic models robust and highly relevant for investigating how anti-cancer therapies elicit responses in the context of the immune system
LIDE has several syngeneic models avalaible:
| Cancer Type | Name of Cell Line |
| Neuroblastoma | Neuro-2a |
| Melanoma | B16-F10 |
| Breast | 4T1 |
| Lung | LLC |
| Liver | Hepa1-6 |
| Gastric | MFC |
| Colorectal | MC38, CT26.WT |
| Sarcoma | K7M2 WT |
| Renal | E.G7-OVA, P388D1, EL4, YAC-1, L5178Y TK+/- clone |
| Lymphoma | (3.7.2C) |
| Myeloma | P3X63Ag8, SP2/0, FO |
| Leukemia | L1210 |
| Mastocytoma | P815 |
| Prostate | RM-1 |
| Testis | MLTC-1 |
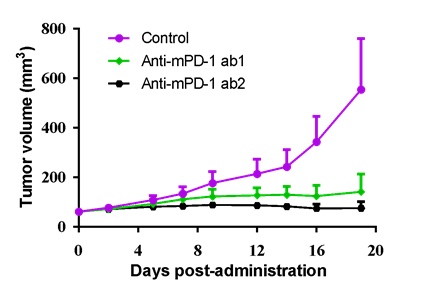
(Table) Available murine cancer cells in LIDE. (Figure) MC38 murine colon cancer cells was inoculated into the right flank in C57BL/6J mice. Two anti-mPD-1 antibody, ab1 and ab2, were given at 5 mg/kg bi-weekly for 6 injections via i.v. or i.p., respectively, and demonstrated good anti-tumor effect.
Similarly, humanized mouse models expedite the evaluation of immunotherapy drug candidates targeting specific human factors by incorporating genetically engineered human targets into a fully immunocompetent host system. Leveraging our humanized mouse models, you can gain insights into your drug's mechanisms of action, kinetics, toxicity characteristics, and potency. This comprehensive understanding empowers you to make informed decisions and select the most promising drug candidate for clinical advancement.
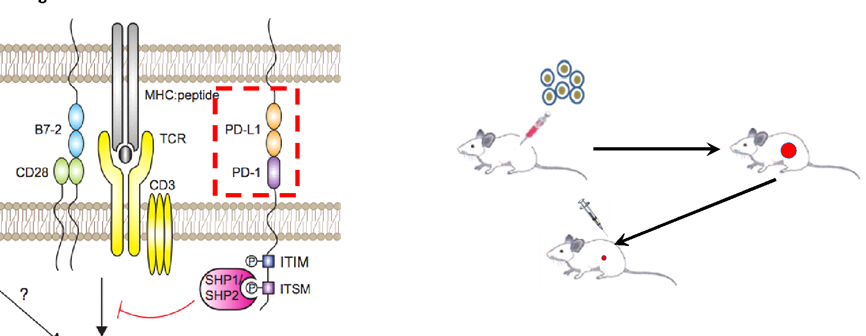
(Left) Extracellular domain of both murine cancer cells (e.g.> PD-L1) and mice (e.g.> PD-1 on murine T cells) were replaced with humanized structure, while the promoter region asd well as intracellular signaling were maintained as previous. (Right) Flowchart of in vivo efficacy in humanized syngeneic models.
| Commercial available GEMM mice |
| huPD-1 | huSIRPα |
| huPD-L1 | huCD47 |
| huCTLA-4 | huTIGIT |
| huTNFRSF4(OX40) | huLAG-3 |
| huCD137(4-1BB) | huTIM-3 |
| huCD27 | huBTLA |
| More TG mice models, feel free to contact LIDE |
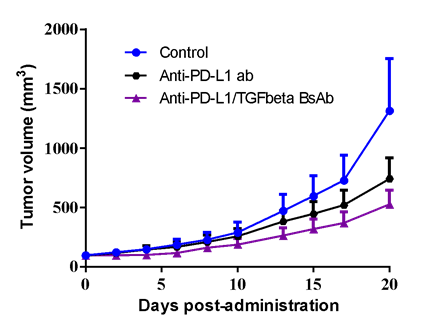
TAA1 overexpressed MC38 murine colon cancer cells (MC38-TAA1) was inoculated into the right flank in huPD-L1 transgenic mice. Both anti-huPD-L1 antibody (3 mg/kg, i.p., bi-weekly for 3 weeks) and anti-huPD-L1/TGFβ BsAb (3.6 mg/kg, i.p., bi-weekly for 3 weeks) demonstrated mediate anti-tumor effect.